FeNO Testing. Made Simple.
Made Affordable. Without Limitations.

Quick and accurate measurement of FeNO. Without the expensive consumables and running costs.
NObreath® provides a quick and reliable way to assess airway inflammation. An adult breathes into the device for twelve seconds and children for ten seconds. The monitor then displays an instant FeNO result in parts per billion which helps healthcare professionals identify raised airway inflammation and guide appropriate asthma treatment.
 NObreath® in Primary Care > |
NObreath® in Primary Care >Reach a diagnosis of Asthma quicker, manage patient medication better, reduce “revolving door patients” and free up valuable clinical time without compromising on quality of care. A quick breath test with instant results. |
 NObreath® in Secondary Care > |
NObreath® in Secondary Care >FeNO testing without the expensive running costs or contractual obligations. Make your department’s budget go further with NObreath® – FeNO testing at just £3.70 per patient! Read More > |
A 12-second test in 4 easy steps.
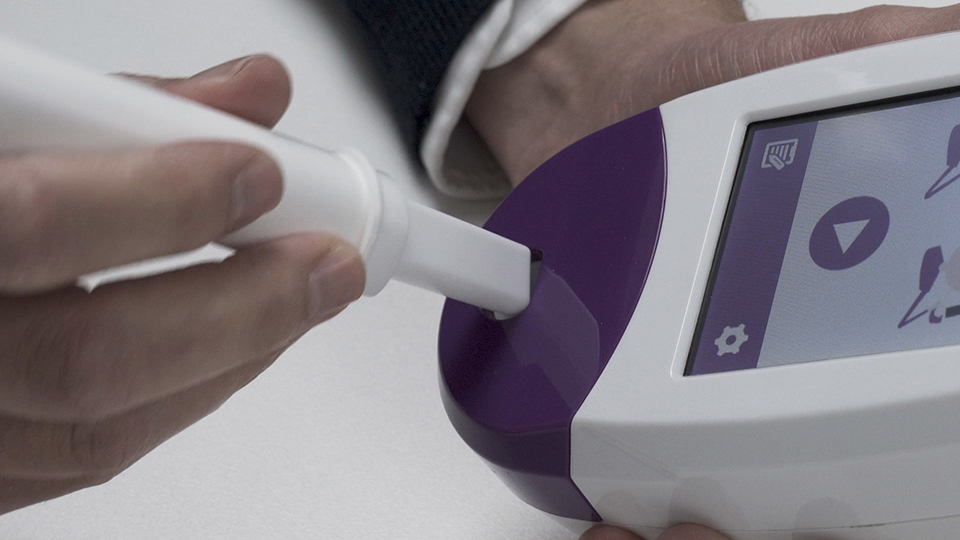

1
The mouthpiece
The NObreath® mouthpiece is supplied individually wrapped and connects securely to the front of the FeNO monitor. Each mouthpiece includes a one way valve and a high quality viral and bacterial filter to support strong infection control standards and reduce the risk of cross infection between patients in clinical settings.
A NObreath® mouthpiece can be reused multiple times by the same patient which helps lower the overall cost per test and supports sustainable FeNO testing in primary care and respiratory services across the UK.
2
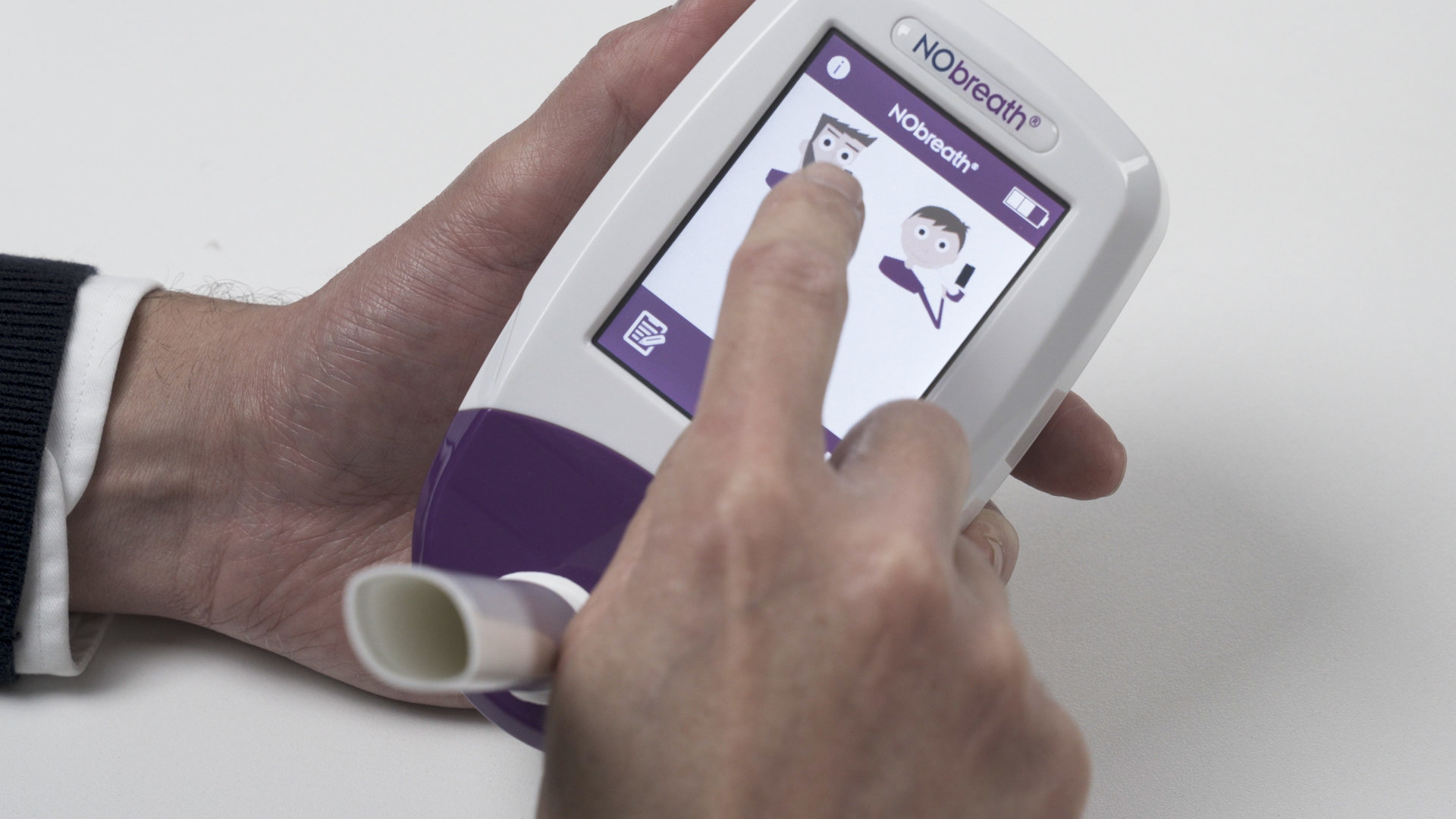
Initiate test
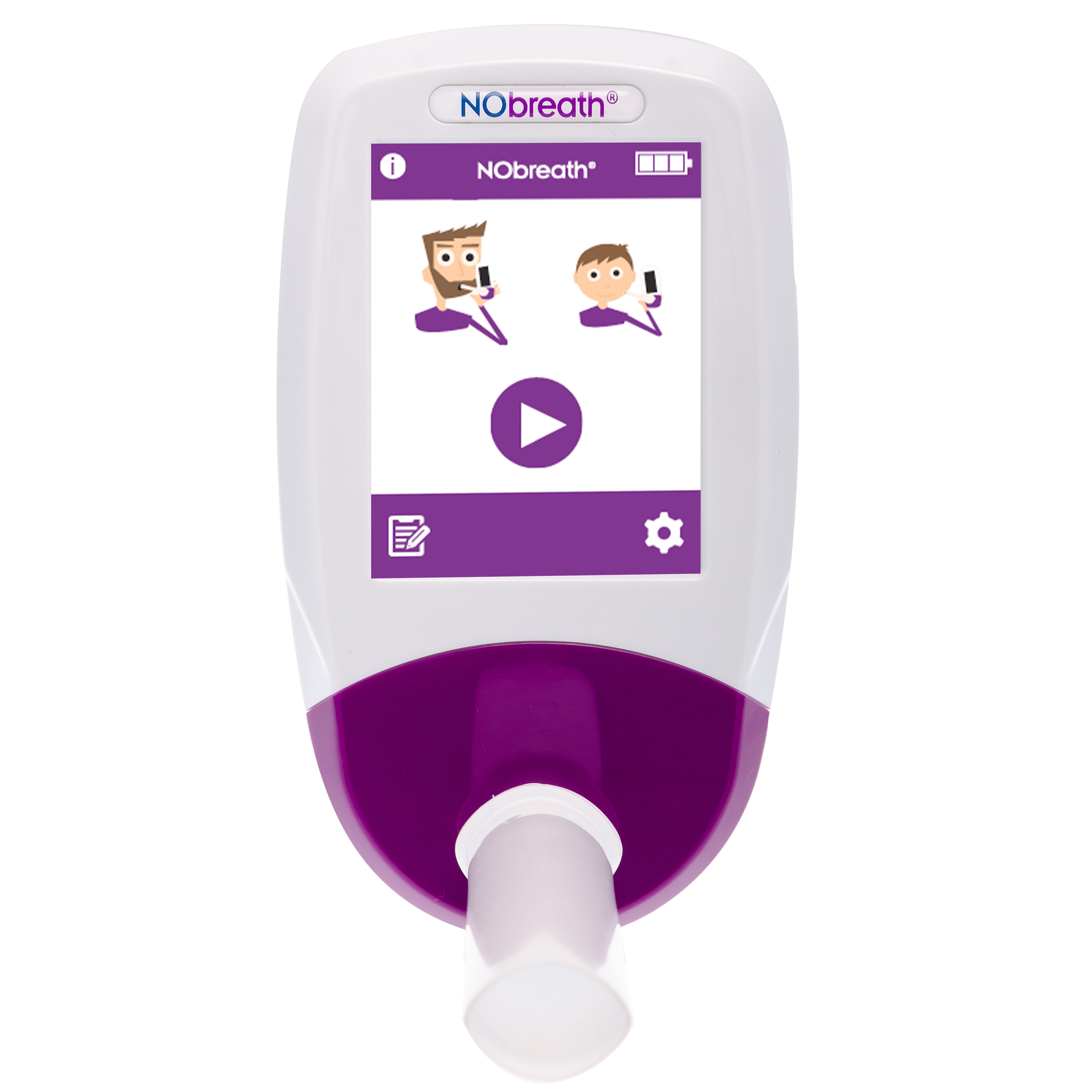
The NObreath® monitor is easy to use with a clear icon based touchscreen display that supports quick operation in busy clinical environments. The device powers on from the button at the top of the unit and has a warm up time of up to sixty seconds.
To begin a FeNO test, select either the adult or child setting on the screen and simply follow the on screen prompts. The guided steps help healthcare professionals carry out reliable FeNO measurements with confidence in both primary care and respiratory clinics across the UK.
3
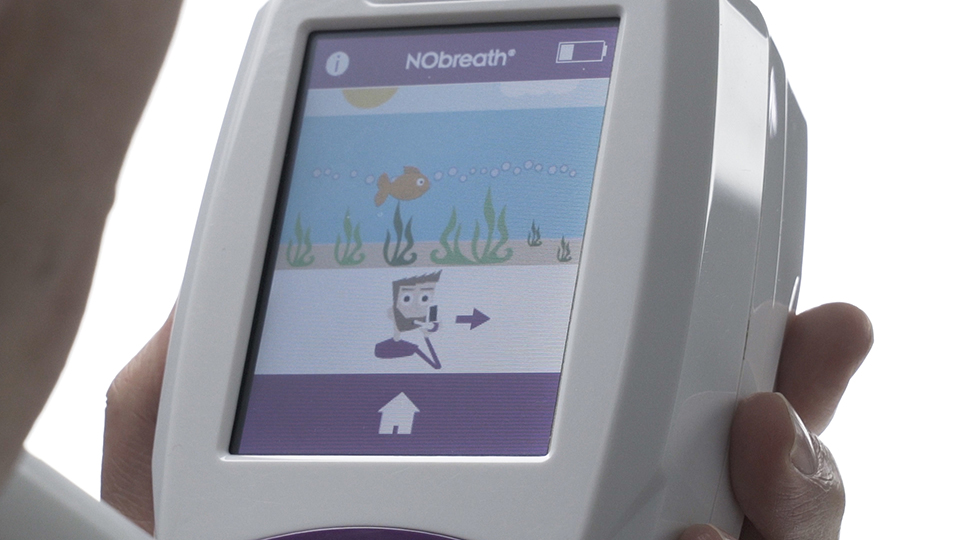
Deep breath in…
When the NObreath® monitor prompts you, take a deep breath in and then exhale through the mouthpiece. The test requires very little respiratory effort. To complete a successful FeNO measurement, the breath needs to be exhaled at a steady flow for the full duration of the test. The gentle resistance in the mouthpiece and the on screen incentive help patients maintain the correct flow and produce an accurate result.
4
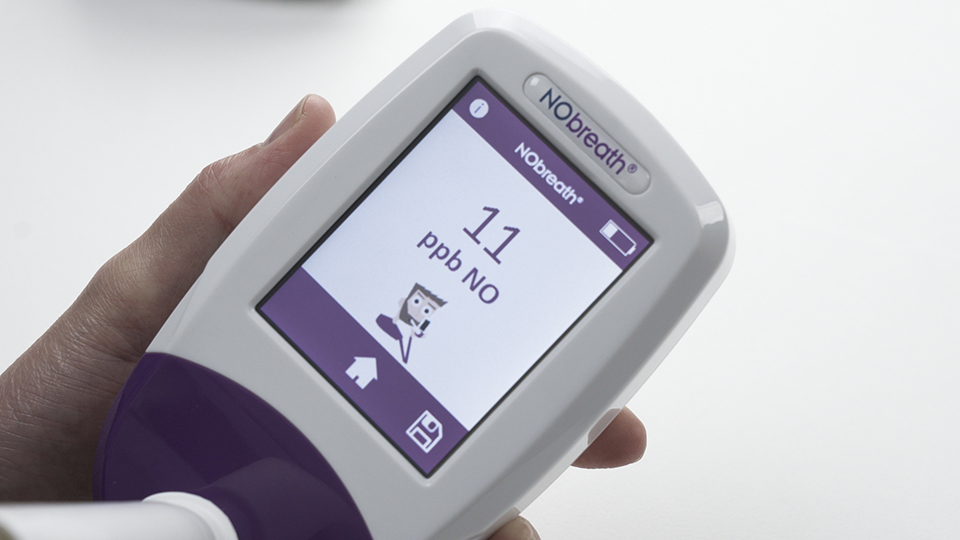
Test complete!
A green tick appears on the screen when the NObreath® monitor confirms a good quality FeNO test. The result is then shown immediately as a single value in parts per billion. In line with NICE guidance, a FeNO level above fifty parts per billion is considered a positive result and indicates that airway inflammation may be present. This supports healthcare professionals when assessing asthma and monitoring response to treatment in UK clinical settings.
Free FeNO Chart PC Software Included
The software supports accurate electronic recording of FeNO measurements with easy to view trending, helping clinicians track airway inflammation over time and monitor patient compliance with prescribed asthma medication. This makes ongoing asthma management simpler and more consistent in primary care and respiratory clinics across the UK.
A built in PDF report feature allows results to be exported and attached to patient record systems in just a few clicks, helping practices maintain clear and reliable clinical documentation.

Key Features
It can be used on adults and children
With simple on-screen prompts, the NObreath® can be used on both adults and children
SIMPLE TO USE TOUCHSCREEN CONTROL
Easy to follow icon based menus on a high resolution screen
Get accurate FeNO readings instantly
Obtain readings quickly, saving precious minutes in appointments
On-screen incentives for patient compliance
Ensures correct usage to obtain a good quality FeNO reading
Recommended
by NICE1
Tried and tested in clinical practice for diagnosis and monitoring of patients with Asthma
NO TEST LIMITS IMPOSED ON THE DEVICE
Low cost of ownership meaning you won’t need to replace the device after a certain amount of tests
Mouthpiece can be used more than once
Unlike other devices, the mouthpiece can be used by the same person more than once
Free PC Software
Download readings directly from the monitor and maintain a history using the free FeNOchart™ software.
Testimonials
Frequently Asked Questions
FeNO stands for fractional exhaled nitric oxide. Higher FeNO levels may indicate eosinophilic airway inflammation. Measuring FeNO can help assess inflammation, monitor response to inhaled corticosteroids and support treatment decisions to improve asthma control.
The NObreath® is a handheld FeNO device used to measure fractional exhaled nitric oxide, an indicator of eosinophilic airway inflammation. FeNO testing can support asthma diagnosis and ongoing management.
The device is suitable for GP surgeries, asthma review clinics, community diagnostic hubs, respiratory services and secondary care settings. It can be used with adults and children for asthma assessment and follow up.
The patient inhales and then exhales steadily into a disposable mouthpiece. The device provides on screen guidance to support a consistent breath sample. The FeNO level displays as a single numerical value in parts per billion.
Yes. The device includes guided prompts that help children maintain a steady breath, making FeNO testing suitable for younger and older patients.
Yes. FeNO testing is recognised in UK asthma guidance. NICE NG245 includes FeNO as part of the diagnostic and monitoring pathway. The British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network also support the use of FeNO to help identify eosinophilic airway inflammation and guide treatment.
Higher FeNO values may indicate eosinophilic airway inflammation and potential responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroids. Lower FeNO levels may indicate controlled inflammation. FeNO results should be interpreted alongside symptoms and clinical history.
A FeNO test typically takes less than one minute including instruction and breath sampling.
Yes. A single patient mouthpiece is used for hygiene and accurate measurement. Each mouthpiece includes a built in bacterial and viral filter.
Only one single patient mouthpiece is required per testing session, and it can be reused multiple times during the same appointment with the same patient. This helps maintain low running costs. Around £3.70 per patient.
Yes. FeNOChart™ PC Software is included as standard. It allows clinicians to store results, compare historical data, review trends and generate PDF reports to support follow up and shared decision making. FeNOchart™ can be downloaded HERE
The device is recommended to be serviced once every 12 months.
No. The device uses a stable electrochemical sensor and does not require calibration gas. This reduces ongoing maintenance and supports cost efficient operation.
The device is covered with a 5 year limited manufacturer’s warranty.